There are no successful operations without effective corrosion management. An effective corrosion management program is key to achieving safety and high reliability in oil and gas production and operations.
Companies today rely heavily on expensive and invasive maintenance and inspection practices that often fail to spot early signs of pipeline corrosion. For these purposes, it is essential to implement appropriate corrosion management best practices and preserve the pipelines. The study estimates that monitoring, replacing, and maintaining assets incur an average annual corrosion-related cost of $7 billion.
Pipelines are essential in transporting gases and liquids over long distances from their sources to their ultimate consumers. Although most companies have access to information and expertise on corrosion damage mechanisms and their prevention methods, the question is, why do pipelines leak and breakdowns, and why do accidents due to corrosion continue to occur?
The corrosion management system prevents catastrophic damage and maintains the safe and reliable operation of your equipment and pipelines. This article will discuss corrosion, its consequences, and methods and solutions for successful corrosion management.
What is corrosion?
Corrosion is a natural phenomenon. It is the material wearing and decomposing process under specific mechanical, chemical, biological, and environmental influences.
In the oil and gas industry, various gases, water, and salts are integral to the exploitation of fluids, which are very corrosive mediums. Different corrosion types occur depending on the material and the environment in which the pipeline is located.
Water, oxygen, hydrogen sulfide, and microorganisms present in their impurities affect equipment and pipeline damage. It is crucial to know the types of corrosion, the mechanisms of the corrosion process, and the corrosion testing method to enable adequate protection.
Corrosion occurs in all oil industry phases – in the primary and secondary production, refining, transport, storage, and distribution.
Consequences of damage caused by corrosion:
- Interruption of gas supply during damage repair – this directly affects the industry’s business and the households,
- Various ignitions and explosions,
- In case of oil pipeline damage, it is possible to interrupt the regular operation of refineries, tanker downtime, and shortage of petroleum products, which leads to additional costs and environmental pollution.
Corrosion types on pipelines
Pipeline corrosion can occur inside and outside the pipe. Many different corrosion types can develop in pipelines. They range from galvanic, pitting, crevice, high-temperature corrosion, and microbial-influenced corrosion.
Galvanic Corrosion
This is the most common form of corrosion. It occurs when two different metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte. Several factors affect galvanic corrosion, including types of metals, the relative size of anode, and environment (humidity, salinity, temperature, etc.).
Crevice Corrosion
Crevice corrosion is the name for the corrosion phenomenon in the narrow surface cracks (crevices). These are the places where impurities and water gathers, the solution’s acidity increases, the pH decreases, and the concentration of aggressive factors contributing to corrosion increases.
Biocorrosion
Biocorrosion or microbiologically influenced corrosion is pipeline corrosion caused by microbiological action. There are two bacteria strains and over five types of bacteria: aerobic, anaerobic, or bacterial, which reduce sulfur. Hydrocarbons serve as a “food source” for bacteria. Depending on the temperature and water presence, bacteria’s action leads to iron oxidation, and thus occurs corrosion inside and outside the pipeline.
Pitting Corrosion
This is the most destructive form of corrosion in the oil and gas industry and often attacks pipelines. Pitting provokes very deep perforations in the material that can cause fractures of fundamental structural elements.
High-temperature Corrosion
High-temperature corrosion is a deterioration of a metal due to heating. This type of corrosion occurs when a metal is subjected to a hot atmosphere in oxygen, sulfur, or other compounds capable of oxidizing the material.
Regardless of the type of corrosion, each form can lead to structural damage, losses, costly repairs, destroyed or contaminated products, employee risks, environmental damage, and a negative impact on a company’s reputation
Methods of corrosion protection in the oil and gas industry
Corrosion protection plays a significant role in the maintenance functionality, productivity, and safety of materials, people, and the environment. Most corrosion damage can be prevented by applying appropriate protection methods from corrosion.
Rust and other forms of corrosion can lead to safety issues and ruin pipeline and supply integrity. Fortunately, various measures and methods exist to minimize corrosion and its consequences.
Protective coating
Protective coatings such as paint, plastic, or powder are the cheapest and most straightforward way to prevent corrosion. All this creates a thin film that acts as a protection for metal surfaces. The base layer of color acts as an inhibitor, and the topcoat resists environmental factors.
Before this procedure, it is essential to prepare the surface (pipeline) – remove impurities by mechanical, chemical, electrochemical processes or degreasing. The most significant disadvantage of coatings is that they often need to be removed and appropriately re-applied. Layers can also contain volatile organic compounds, making them susceptible to corrosion.
Cathodic protection
In practice, effective cathodic protection against galvanic corrosion is the most widely used. This method converts active sites on a metal surface to passive sites by giving electrons from another source, usually with galvanic anodes attached to or near the surface.
The metals used for the anodes are aluminum, zinc, or magnesium. This method’s disadvantage is that the anodes must be checked frequently, increasing maintenance costs.
Hot-dip galvanizing
This method of preventing corrosion involves immersing the steel in molten zinc. This provides adequate corrosion protection for steel parts and assemblies. The hot-dip galvanizing method has been used for over 250 years, and due to the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of the procedure, it is one of the most widely used forms of corrosion protection.
Some pipelines may be too large for this procedure, which is one of the disadvantages. Incorrectly performing the process can crush or peel off the zinc, resulting in increased maintenance inspections and additional costs.
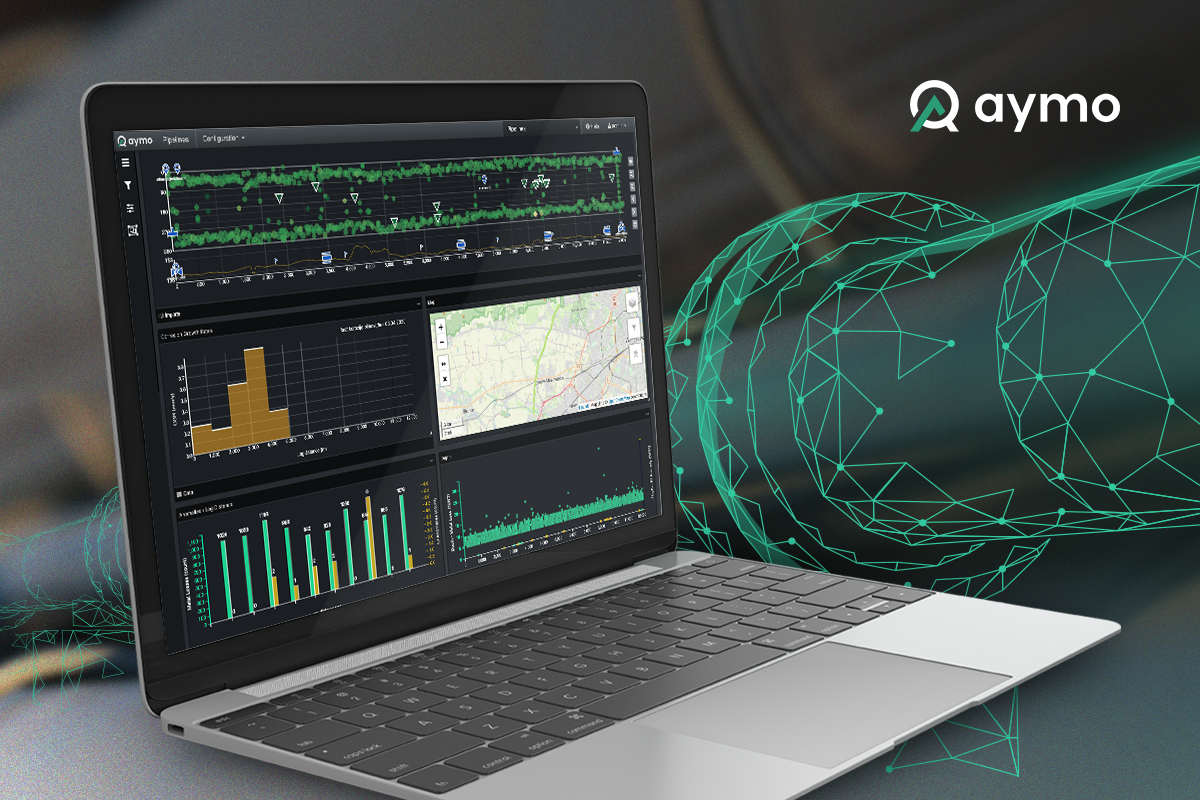
Pipeline integrity management software
Aymo is state-of-the-art pipeline integrity management software for pipeline visualization, management and maintenance, asset integrity, and workflows in the oil and gas industry. The system provides an overview and status of each pipeline, plans repairs on time, and simulates future corrosion growth.
Aymo uses advanced algorithms that allow users to predict corrosion growth over their pipelines, make timely decisions, and save time and reduce costs.
In addition to the available chemical treatment products, corrosion-resistant materials, protective coatings, and cathodic protection, it is essential to emphasize the importance of inspection, network monitoring, and corrosion consulting expertise.
Successful corrosion management solution
Safety has become an integral part of an organization’s management system in the oil and gas industries.
Corrosion management ensures safer and longer-lasting protection of assets such as pipelines, increases return on investment (ROI) while reducing costs, risks and preserving the environment. Corrosion protection is one of the most critical prevention measures.
All parts at risk of corrosion are protected by anti-corrosion protection (cathodic protection or coatings) to prolong the service life and reduce the likelihood of damage and leaks. Reducing the costs associated with corrosion requires much more than technology. It requires aspects of changing how corrosion decisions are made within an organization.
Corrosion Management Program
A Corrosion Management Program is a set of processes and documented procedures required for planning, executing, and continually improving an organization’s ability to manage the threat of corrosion for existing and future assets and associated systems.
Lack of proper metrics, plans, and corrosion management can lead to improper allocation of budget funds. To avoid these situations, implement corrosion management elements into your entire management system.
An innovative solution that can help you is AYMO, the pipeline integrity management software that provides a complete corrosion detection and control service. AYMO provides a unique and modular solution for the oil and gas industry in pipeline monitoring.
At Feromihin, we help clients control corrosion of oil and gas assets by implementing a Corrosion Management Program (CMP). Corrosion never stops, but we can control it by developing and implementing a CMP.
With our rich experience in the oil and gas industry, we help reduce risk, achieve corrosion control and apply best practices in the oil and gas business through consulting. We want to provide our customers with the best available method of corrosion protection management.
Identify and prevent pipeline corrosion before it becomes a problem. Contact us today to ensure your asset’s integrity and security and implement a Corrosion Management Plan.






 Hrvatski
Hrvatski